Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis among the elderly population, and it is also one of the most constant causes of physical disability among older folks. The disease affects both genders, being more common in men before the age of 45 years, and more common in women after the age of 45 years. Continue reading the following blog post to find out more about the condition and several other arthritis types.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis symptoms can range from stiffness to light pain that comes and goes to acute pain in the joint. Some of the most common signs include tenderness and swelling, joint pain, a crunching feeling or sound of bone rubbing on bone, and stiffness after getting out of bed. However, not everyone with osteoarthritis will experience pain. The condition usually affects the lower back, neck, hands, and weight-bearing joints like the hips, knees, and feet. Osteoarthritis affects only the joints, and not internal organs.
Causes and Risk Factors of Osteoarthritis
Researchers suspect that the cause of osteoarthritis is a combination of various factors in the environment and our body. The risk of developing osteoarthritis increases as we age. Exerting too much stress on our joints that have been formerly injured, excess body weight, and improper alignment of joints can all contribute to the development of osteoarthritis.
Other Types of Arthritis
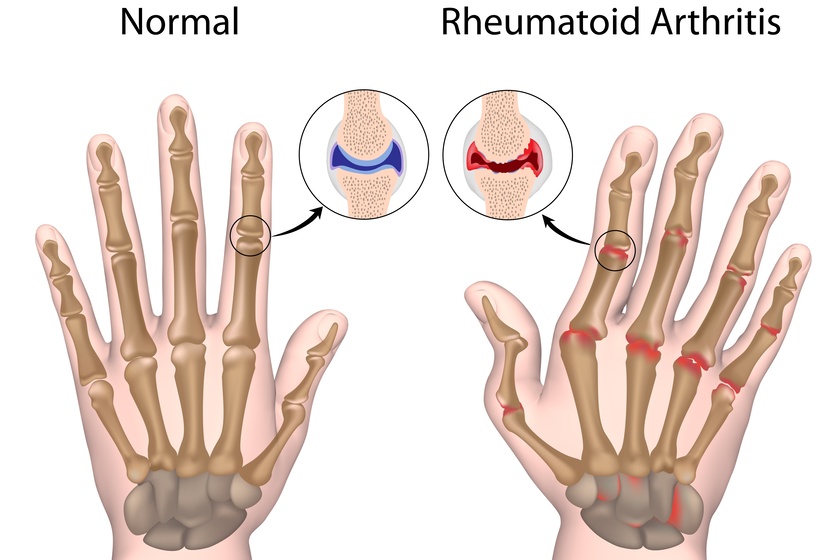
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – An autoimmune and inflammatory disease that involves the immune system attacking healthy cells in the body by mistake, causing painful swelling or inflammation in the affected body parts.
- Childhood Arthritis – Arthritis in children can cause permanent physical damage to the joint which can make it tough for the child to perform day-to-day tasks like dressing or walking and may lead to disability.
- Fibromyalgia – The condition causes pain all over the body and other health problems like fatigue, sleep problems, and mental and emotional distress.
- Gout – It is a common form of inflammatory arthritis that can cause extreme pain. It often affects one joint at a time and there are times when it gets worse and also times when there are no symptoms at all.
- Psoriatic – An autoimmune inflammatory disease that involves the immune system attacking the skin and joints to cause pain and skin rashes.
Preventing Arthritis
Exercise, diet, and smoking are all major factors to help prevent arthritis. A person can switch to a low-fat, anti-inflammatory, well-balanced diet that is rich in omega-3 fatty acids. They should also make sure to stay active to keep their joints moving. Exercising will also help them to maintain a moderate weight which will not exert too much stress on the joint, thus reducing the risk of developing arthritis.
Medical Consultation for Arthritis
If a person starts to experience pain in a joint which does not go away within several days, they should consult their physician. Arthritis is a progressive condition, so it can cause greater damage if more time passes before treatment starts. Physicians may recommend medication for pain relief and to slow down the progression of the condition. In some cases, patients may be recommended to go for a surgery to repair joints that have sustained severe damage.